At Reputation911, we help you remove unwanted content appearing under your name in search engines and across the internet. Our team works to suppress negative or outdated information, reclaim authoritative mentions, and ensure that your digital presence reflects the image you want to project.

Seeing something about yourself online that you don’t want others to see can feel overwhelming.
It might be a photo you regret, an old post that no longer reflects who you are, or personal details that should have stayed private.
Whatever it is, it can leave you feeling exposed, anxious, and powerless.
The internet can feel like a permanent archive, but you’re not stuck with it forever.
Whether it’s a blog, news, image, or video, this article will guide you through the process of removing unwanted content from a website or social media platform on the internet – so you can protect your privacy and take back control of your personal and professional life.
This involves working directly with website administrators, taking legal action, or deleting content that you control. Follow these steps.
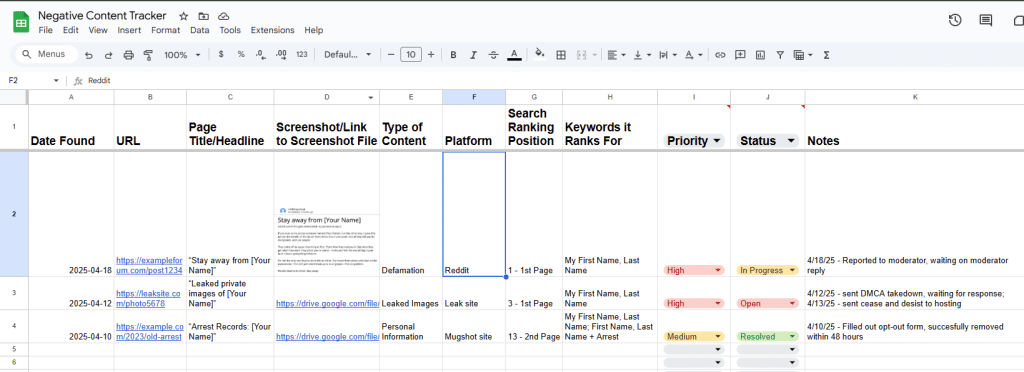
Before getting started, you need to find everything that’s out there and document it.
Keeping a record of the harmful content will help you stay organized and track your progress (or you can bring that information to an online reputation management professional).
Set up a Google Doc or spreadsheet to track every piece of content you want to remove.
For each link, include:
To find negative content, open an incognito (private browsing) window and Google yourself using:
This will give you a more accurate view of what others see when they search for you.
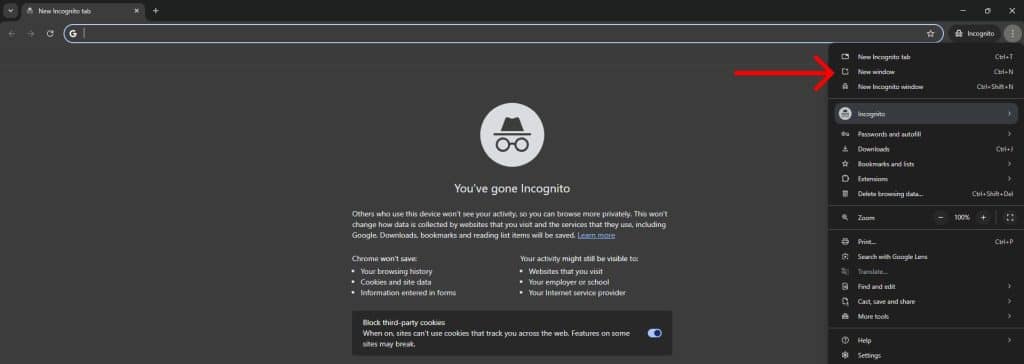
Important tip:
Use incognito mode during this step. Googling yourself in a regular window may push negative content further up in rankings. Plus, the regular window tailors your search results, giving you a skewed view.
Start by cleaning up the content you directly control or manage. This is the fastest and most effective way to reduce your digital footprint.
Focus on these areas:
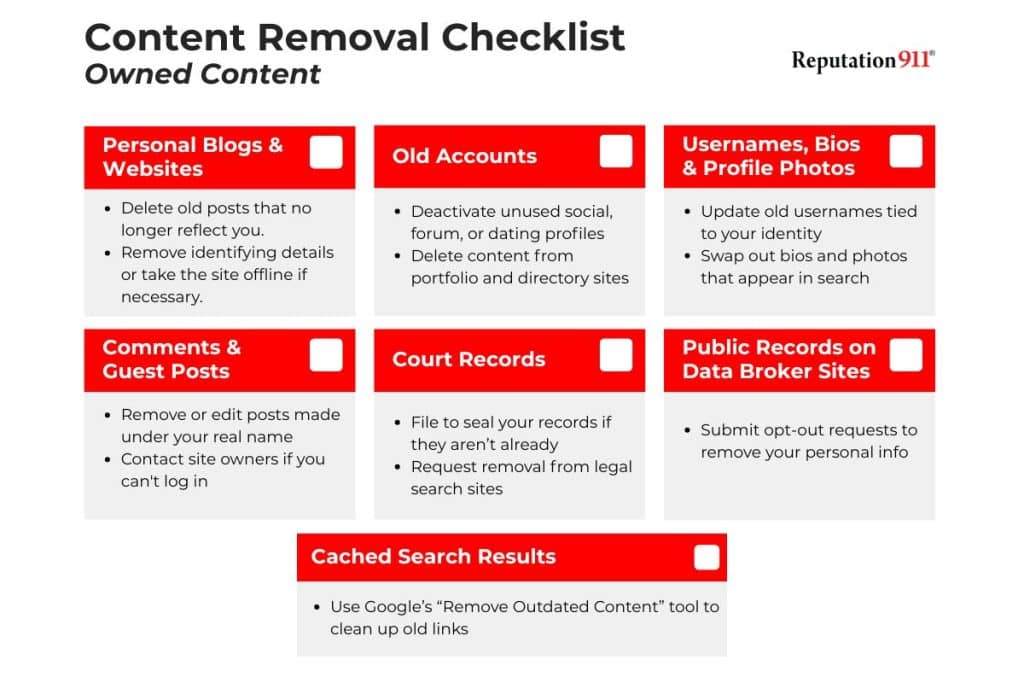
One of the easiest ways to refresh your digital footprint is to clean up your social media accounts.
Even if the content you’re worried about right now isn’t on your profiles, your social media history can still impact your reputation.
Employers, clients, and even acquaintances often check social media before making decisions about you – so it’s important to make sure you remove things that could come back to haunt you.
Important tips:
If the content is on a specific website, forum, or social media platform (like Facebook, Twitter, Reddit, etc.), contact the website’s administrator or support team and request the removal of the content
If the content is on a blog or website you don’t control, contact the publisher or site admin to request removal.
Be polite, clear, and direct. If the content violates your rights or harms your reputation, explain why. Support your request with legal or policy-based reasons, like:
It also helps to reference Google’s content removal policies, since publishers may respond better when they understand how it could impact their visibility.
When you reach out, include:
Struggling with news coverage or online press? Read our full guide on removing negative news articles from Google when publishers won’t cooperate.
If full removal isn’t an option, ask the publisher to update or correct the content. This works best when the page is outdated, misleading, or missing key context.
Ask the publisher to:
Keep your tone respectful and professional.

If your content appears at the top of a Google search, you may be able to remove it. However, removing unwanted search results may only apply to specific conditions, situations, and types of content that are sensitive, harmful, or illegal.

Google won’t delete just anything from search results, but they do accept removal requests for the following:
For more tips on removing personal details like your name, phone number, or home address, visit our guide on how to remove personal information from Google.
If content violates your rights, is defamatory, or breaches terms of service, consider legal action. For copyright issues, privacy violations, or defamation, you may request removal or file a DMCA takedown notice.
Before taking legal action, it’s important to evaluate the content in question:
| Type of Content | Definition | Examples | Recommended Legal Action |
| Infringing on Intellectual | Intellectual property rights protect creations like inventions, artistic works, and brand names, and infringement occurs when these are used without permission. | – Copyright Infringement: Using copyrighted images or music without permission. – Trademark Infringement: Selling goods with a logo similar to a registered trademark, like copying Nike’s “swoosh.” | 1. Send a DMCA Takedown Notice (for copyright infringement) 2. File a trademark infringement complaint 3. Seek cease-and-desist letter or legal action |
| Defamatory Content | Defamation is making false statements presented as facts that harm someone’s reputation. Defamation can be spoken (slander) or written (libel). | – Falsely claiming on social media that someone is involved in illegal activities, damaging their personal reputation (slander example). – A website publishes a false article claiming a business owner committed fraud (libel example). | 1. Send a cease-and-desist letter 2. File a defamation lawsuit for damages 3. Request correction or retraction of the false statements |
| Violating Privacy | Privacy violations occur when personal information is disclosed or used without the individual’s consent, breaching their right to control how their personal data is shared or used. | – Personal Data Disclosure: Posting someone’s address, phone number without permission, or other personal details online without consent. – Invasion of Privacy: Sharing intimate images or videos of someone without their permission. | 1. Send a cease-and-desist letter 2. File a privacy violation lawsuit 3. Request removal under applicable privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) |
| Illegal Content | Illegal content includes material that violates the law, such as content that promotes criminal activity or violates public safety standards. | – Illegal Sale of Items: A website selling counterfeit goods, illegal drugs, or firearms. – Hate Speech: A social media account spreading messages that incite violence or discrimination against a group based on race, religion, or ethnicity. | 1. Report to law enforcement or platform for illegal activity 2. Request immediate removal and report to relevant authorities (e.g., FBI, FTC) |
Websites typically have terms of service (TOS) that outline acceptable content and user behavior.
You should review these terms to understand:
The website’s process for removing harmful or illegal content.
The next step is often to contact the website owner or platform that hosts the content.
Here’s how to approach it:
If the content violates your copyright, you can send a Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) takedown notice to the website or hosting service.
The notice should include:
Most websites, especially large platforms (like YouTube, Facebook, or Instagram), have a process for submitting DMCA takedown requests.
If the content is not removed after filing a DMCA request, or if the takedown notice is ignored or disputed, you may need to consider filing a lawsuit for copyright infringement. Legal action can help recover damages and potentially stop further unauthorized use of your work.
What can you do if you can’t remove content from the internet?
If removal isn’t possible on your own, you can still take next steps while pursuing legal action (if appropriate).
While legal action can be costly or timely, suppression can help greatly reduce the likelihood of people finding negative content about you in search results.
Search engine suppression is the process of pushing down unwanted or harmful search results by boosting positive, relevant content that you control.
The goal is to move negative content off the first page of Google – where fewer people will see it.
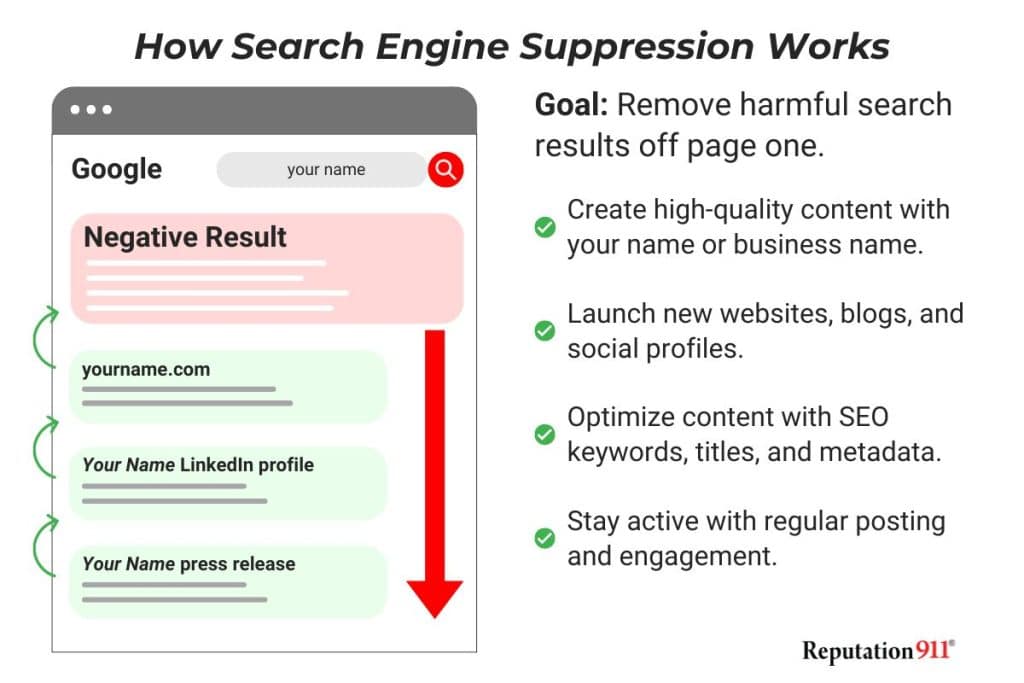
Here’s how it works:
Suppression doesn’t erase the original content, but it makes it much harder to find. Get more strategies to bury negative content in search results.

You don’t have to live with the stress of negative content circulating on the internet forever. You’re not alone, and you do have options.
Key Takeaways:
At Reputation911, we offer specialized online content removal services to help individuals and businesses take back control of their online image.
Don’t let negative content define you. Call Reputation911 at 866-697-3791 for a free consultation & quote.
Sometimes, yes—but it depends on where the content is posted and who controls it. If you don’t own the website or account, you can request removal, but there’s no guarantee the host will comply. When removal isn’t possible, you can often remove it from Google search results or suppress it so it’s much harder to find.
Start by removing it at the source. Contact the website owner, platform, or administrator and request that the post, image, or page be deleted. If you control the account (like social media), delete it directly—then use Google’s tools to clear cached/outdated versions.
If the site owner doesn’t respond or refuses to remove the content, you still have options. You can file a removal request with Google if the content violates privacy, copyright, or legal policies, or use search engine suppression to push the result off page one so it’s far less visible.
Yes. Google can de-index a page or image from search results if it meets their removal criteria (such as personal information, explicit images, copyright infringement, or pay-to-remove schemes). The content may still exist on the website, but it won’t appear in Google searches.
Once content is removed from the source, Google typically updates its index within a few days to a few weeks. Using Google’s “Remove Outdated Content” tool can speed up the process, but full removal may take up to 30 days in some cases.
Removal eliminates content from the source or from Google’s index entirely. Suppression doesn’t delete the content—it uses SEO strategies to push unwanted results off the first page of search results, where most people never look. Both approaches are often used together.